Group Activity Recognition
Table of Contents
- Key Updates
- Usage
- Dataset Overview
- Ablation Study
- Performance Comparison
- Interesting Observations
- Model Architecture
Key Updates
- ResNet50 for feature extraction (replacing AlexNet).
- Ablation studies to analyze model components.
- Implementation of an end-to-end version (Baseline 9).
- Achieve higher performance across every model baseline compared to the original paper.
- Full implementation in Python (original used Caffe).
Usage
1. Clone the Repository
| |
2. Install the Required Dependencies
| |
3. Download the Model Checkpoint
This is a manual step that involves downloading the model checkpoint files.
Option 1: Use Python Code
Replace the modeling folder with the downloaded folder:
| |
Option 2: Download Directly
Browse and download the specific checkpoint from Kaggle:
Group Activity Recognition - PyTorch Checkpoint
Dataset Overview
The dataset was created using publicly available YouTube volleyball videos. The authors annotated 4,830 frames from 55 videos, categorizing player actions into 9 labels and team activities into 8 labels.
Example Annotations
- Figure: A frame labeled as “Left Spike,” with bounding boxes around each player, demonstrating team activity annotations.
Train-Test Split
- Training Set: 3,493 frames
- Testing Set: 1,337 frames
Dataset Statistics
Group Activity Labels
| Group Activity Class | Instances |
|---|---|
| Right set | 644 |
| Right spike | 623 |
| Right pass | 801 |
| Right winpoint | 295 |
| Left winpoint | 367 |
| Left pass | 826 |
| Left spike | 642 |
| Left set | 633 |
Player Action Labels
| Action Class | Instances |
|---|---|
| Waiting | 3,601 |
| Setting | 1,332 |
| Digging | 2,333 |
| Falling | 1,241 |
| Spiking | 1,216 |
| Blocking | 2,458 |
| Jumping | 341 |
| Moving | 5,121 |
| Standing | 38,696 |
Dataset Organization
- Videos: 55, each assigned a unique ID (0–54).
- Train Videos: 1, 3, 6, 7, 10, 13, 15, 16, 18, 22, 23, 31, 32, 36, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 48, 50, 52, 53, 54.
- Validation Videos: 0, 2, 8, 12, 17, 19, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 33, 46, 49, 51.
- Test Videos: 4, 5, 9, 11, 14, 20, 21, 25, 29, 34, 35, 37, 43, 44, 45, 47.
Dataset Download Instructions
- Enable Kaggle’s public API. Follow the guide here: Kaggle API Documentation.
- Use the provided shell script:
| |
For further information about dataset, you can check out the paper author’s repository:
link
Ablation Study
Baselines
B1: Image Classification:
A straightforward image classifier based on ResNet-50, fine-tuned to classify group activities using a single frame from a video clip.B3: Fine-tuned Person Classification:
The ResNet-50 CNN model is deployed on each person. Feature extraction for each crop 2048 features are pooled over all people and then fed to a softmax classifier to recognize group activities in a single frame.B4: Temporal Model with Image Features:
A temporal model that uses image features per clip. Each clip consists of 9 frames, and an LSTM is trained on sequences of 9 steps for each clip.B5: Temporal Model with Person Features:
A temporal extension of the previous baseline (B3) temporal on crops (LSTM on player level), where person-specific features pooled over all individuals to recognize group activities.B6: Two-stage Model without LSTM 1:
Individual features pooled over all people are fed into an LSTM model to capture group dynamics.B7: Two-stage Model without LSTM 2:
The full model (V1) trains an LSTM on crop-level data (LSTM on a player level). Clips are extracted: sequences of 9 steps per player for each frame. A max-pooling operation is applied to the players, and LSTM 2 is trained on the frame level.B8: Two-stage Hierarchical Model:
The full model (V2) trains an LSTM on crop-level data (LSTM on a player level). Clips are extracted as sequences of 9 steps per player for each frame. A max-pooling operation is applied to each player’s team in a dependent way. Features from both teams are concatenated along the feature dimension, and the result is fed to LSTM 2 at the frame level.B9: Unified Hierarchical Model:
In earlier baselines, person-level and group-level activity losses were addressed independently, leading to a two-stage model. Baseline 9 integrates these processes into a unified, end-to-end training pipeline. This approach enables simultaneous optimization of both person-level and group-level activity classification through a shared gradient flow. Additionally, Baseline 9 employsResNet34instead ofResNet50andGURinstead ofLSTM, reducing model complexity and mitigating the risk of overfitting.
Performance comparison
Original Paper Baselines Score
My Scores (Accuracy and F1 Scores)
| Baseline | Accuracy | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline 1 | 72.66% | 72.63% |
| Baseline 3 | 80.25% | 80.24% |
| Baseline 4 | 76.59% | 76.67% |
| Baseline 5 | 77.04% | 77.07% |
| Baseline 6 | 84.52% | 83.99% |
| Baseline 7 | 89.15% | 89.14% |
| Baseline 8 | 92.30% | 92.29% |
| Baseline 9 | 93.12% | 93.11% |
Interesting Observations
Effect of Team Independent Pooling
The following confusion matrices from Baseline 5 and Baseline 6 reveal some interesting insights:
Baseline 5 Confusion Matrix

Baseline 6 Confusion Matrix

- The most frequent confusions occur between:
- Right winpoint vs. left winpoint
- Right pass vs. left pass
- Right set vs. left set
- Right spike vs. left spike
This behavior is likely due to the pooling of the 12 players from both teams when transitioning from the individual/personal level to the frame/group level. By grouping all players into one unit, the model loses valuable geometric information regarding player positions.
When the teams are grouped and processed individually before concatenation, the player position information is retained. This suggests that a more careful handling of player positions could improve model performance, as observed in Baseline 8 and Baseline 9.
Baseline 8 Confusion Matrix

Baseline 9 Confusion Matrix
/outputs/Group_Activity_Baseline_9_eval_on_testset_confusion_matrix.png)
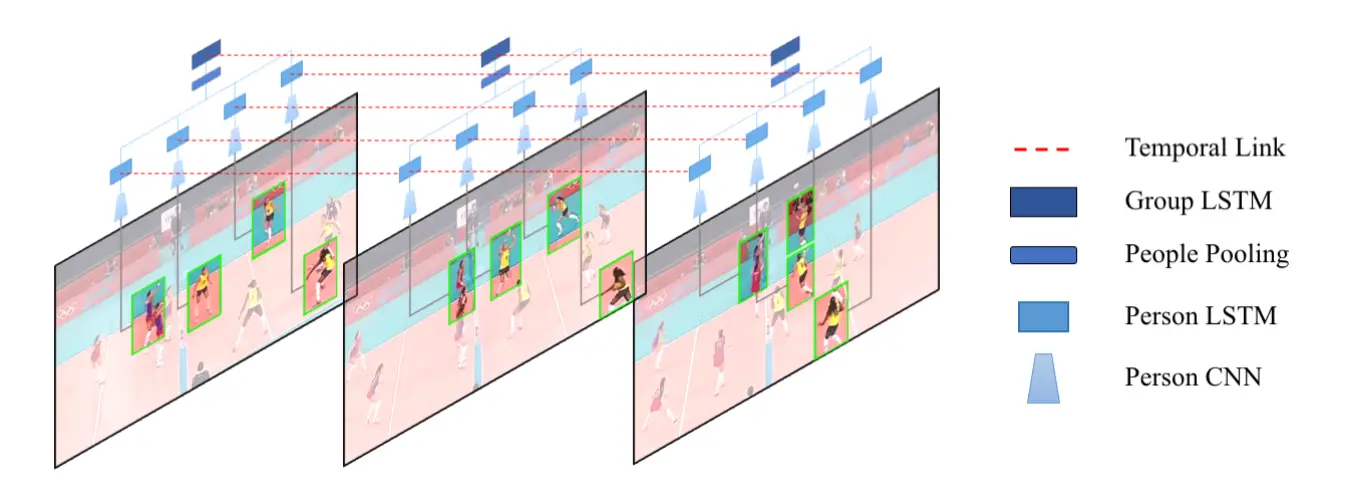
Model Architecture (Baseline 8)
The baseline model architecture for temporal group activity classification is designed to integrate individual player features and team-level dynamics over time. This section provides a detailed description of the components and processing stages of the model.
- Player-Level Feature Extraction: Individual player features are extracted and processed over time using ResNet-50 and LSTM.
- Team-Level Feature Integration: Features from both teams are aggregated and processed further using a second LSTM to classify the group activity.
1. Player Activity Temporal Classifier
The Person_Activity_Temporal_Classifier is responsible for extracting features for individual players from input sequences of video frames. It consists of the following components:
- ResNet-50 Backbone: Pretrained ResNet-50 (excluding the final fully connected layer) is used to extract spatial features for each player from image crops.
- Layer Normalization: Applied to stabilize and normalize the extracted features.
- Temporal Modeling with LSTM: An LSTM processes the sequence of features for each player, capturing temporal dependencies.
- Fully Connected Layers: A series of dense layers map the LSTM outputs to the target activity classes.
2. Group Activity Temporal Classifier
The Group_Activity_Temporal_Classifier extends the player-level classifier to incorporate team-level dynamics:
- Shared ResNet-50 and LSTM: The ResNet-50 and LSTM from the
Person_Activity_Temporal_Classifierare shared, with frozen parameters to leverage pretrained weights. - Pooling and Feature Concatenation:
- ResNet-50 and LSTM outputs for individual players are concatenated along the feature dimension.
- Features are grouped into two teams (e.g., players 1–6 for Team 1 and players 7–12 for Team 2).
- An adaptive max-pooling layer aggregates player features within each team.
- Features from both teams are concatenated.
- Team-Level LSTM: A second LSTM processes the concatenated team-level features over time, capturing temporal dependencies between team interactions.
- Classification Layers: Fully connected layers map the LSTM outputs to the final group activity class.
Training Configuration
- Training Platform: The model is trained on Kaggle’s free GPU quota (P100 16 RAM GPU) Notebook.
- Optimizer: AdamW optimizer with learning rate scheduling.
- Batch Size: 8
Model Architecture: Hierarchical Group Activity Classifier (Baseline 9)
The Hierarchical_Group_Activity_Classifier combines spatial feature extraction, temporal modeling, and hierarchical aggregation to provide predictions at both the individual and group levels.
Feature Extraction:
- A pretrained ResNet-34 extracts spatial features from individual video frames.
Individual-Level Classification:
- Extracted features are normalized (
Layer Normalization) and passed through a Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) to capture temporal dependencies for each bounding box across frames. - The temporal output is classified into individual activity classes using a fully connected network comprising multiple layers with normalization, activation, and dropout.
- Extracted features are normalized (
Group-Level Classification:
- Features from individuals are pooled into team representations using adaptive max pooling, splitting individuals into predefined groups.
- The pooled features are normalized and passed through another GRU to capture higher-level temporal dynamics at the group level.
- A similar fully connected network classifies the group activities.
Outputs:
person_output: Predictions for individual activity classes.group_output: Predictions for group activity classes.
Training Configuration
- Training Platform: The model is trained on Kaggle’s free GPU quota (X2 T4 15 RAM GPU) Notebook.
- Optimizer: AdamW optimizer with learning rate scheduling.
- Batch Size: 8